Design Cotter Joint or Socket and Spigot Joint
 |
| 3D view of cotter joint |
 |
figure 1
|
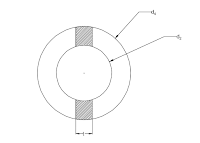
This diagram called cotter joint or socket and spigot joint. It consist a three main parts
- socket
- spigot
- cotter
It is used in both type of load tensile load and compressive load.
d = diameter of shaft,
d1 =
outer diameter
d2 =
internal diameter of socket = external diameter of spigot,
d3 =
diameter of spigot collar,
d4 =
diameter of socket collar,
a = distance from End of slot to end of rod.
c = approximately thickness of socket collar,
e = thickness of socket,
t1 = thickness of spigot collar,
t = thickness of cottar.
Designing procedure of Cotter - Joint :
When ever any component we have to check where failure will take place. It means failure is going to take place at that regain where we have internal weakness or if small area because if area is small at that location stress will be maximum and material will be failing at that small area so, It will fail due to internal creaks, it will fail if there is hole or any kind of slot in that part and object can fail if it has less area.
Step : 1 Design of Shaft ( Rod ),
Shaft has smallest diameter of elements. Once we are pulling the rod there are chances of this rod to break along that's diameter and we see thr area after breaking, it look like the cross section area down blow.
A = Resisting Area,
Strength of rod considering tensile failure is given by :
( Strength means the load which any machine part can resist, Strength = load carrying capacity)
σt = tensile stress,
P = tensile load,
From above equation 'b' can be calculate.
Step : 2 Design of Spigot End
Spigot may failure under three condition.
- tension
- shear
- crushing
1. Considering failure of spigot under tension.
Failure occurs at that location where are having holes, slot or any irregularity cracks or minimum dimension.
Spigot may fail along that cotter slot. It can break when the load is applied. When spigot is pulled from shaft side. There are chances that it can break two half at the slot and when we turn it has fail. It has broken in to two parts. when we turn it then the area we are seeing it would be called as resisting area.
Resisting area = A,
Strength of spigot under tension :
From above equation 'd2' or 't' can be calculated.
2. Considering failure of spigot shearing
When load apply toward right in spigot, there are chances right side part of the spigot from the cotter go along with load and left side part of spigot from the cotter slide opposite side of the load as shown in below figure. That is called shearing action.
Shearing strength of spigot :
Shear stress =
τ
From above equation 'a' can calculated.
3. Considering Crushing of Spigot.
When cotter is inserted in the slot. there is metal-metal rubbing between spigot and cotter. Because of that that spigot would be converted in to fine powder, at that slot some peace of spigot will get disintegrated. It shown in below figure.
Crushing area or Resisting Area = A
Crushing strength of spigot :
From above equation '
σcr
' can be checked.
Step 3 : Design of Spigot Collar
There are chances when load is applied, Spigot collar remain it's position but
d2 diameter portion go along with the load shearing the spigot collar at junction of d2 diameter area and collar.
Shearing Area = A,
Shearing Strength of spigot Collar :
From above equation thickness of collar can be found out.
Step 4 : Design of Socket
1. Consider failure of Socket under tension.
When we have this socket and spigot joint and load is applied at socket move toward right. failure take place where internal slot, cracks, holes or small area. socket has a also slot so it will be failing along the slot in two half and cotter breaking half area look like below.
Resisting Area = A,
Tensile strength of socket
From above equation 'd1' can be calculated.
2. Considering Shearing failure of Socket.
When the load applied right portion of socket go along within load but left portion of socket from cottar it will go in to opposite direction.
It is a case of double Shear ( two surface out there both side of cottar ).
Resisting Area = A,
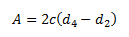
Shearing Strength of socket.
From above equation either 'd4' or 'c' can be calculated.
3. Considering failure under crushing.
When load is applied there is chances to metal-metal rubbing and it will fail under crushing.
Resisting Area = A,
Crushing Strength of socket.
From above equation 'd4' can be calculated.
Step 5 : Design Of Cottar
When we applied load on socket and spigot in opposite direction. There are chance of cottar to shear.
1. Considering shearing failure of cotter.
A = 2bt
Shearing Strength of cottar.
From above equation 'b' can be calculated.




























0 Comments